

Next: Intrinsic reaction coordinate
Up: Reaction path
Previous: Reaction path
Contents
The most intuitive strategy to draw a MEP is to identify an internal coordinate (bond
distance, angle, dihedral ...) or any combination of them as a reaction coordinate,
and then to perform several restrained
energy minimizations at different values of this coordinate kept frozen.
At every restrained minimization this coordinate
is modified, going from reactant to product, in order to have a discontinuous
representation of the supposed reaction path.
The way this coordinate is fixed is usually applying a harmonic potential with a force
constant big enough to keep unmoved the atoms involved in internal coordinate.
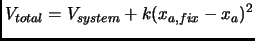 |
(2.88) |
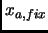 is the intended fixed value at each restrained minimization,
is the intended fixed value at each restrained minimization,
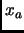 is the current value of the reaction coordinate along the simulation.
The above expression can be generalized to a combination of variables [140].
is the current value of the reaction coordinate along the simulation.
The above expression can be generalized to a combination of variables [140].
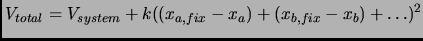 |
(2.89) |
This method is also useful when we want to discriminate between a concerted or stepwise
mechanism, where, in this case, a and b are those coordinates governing
the two reaction steps.
This last option is the best since only one degree of freedom is kept unmoved
while contemplating both distances variation.
The point of maximum potential energy along the reaction coordinate can
be taken as a first approach to the transition state structure. However,
it is not always so easy or intuitive to identify an internal coordinate as the reaction coordinate.
If the coordinate is not appropriate we cannot be sure of visiting the saddle point region. In any case, even
when a coordinate seems to be intuitive, it should be always checked if the Hessian
matrix has an unique negative eigenvalue that will be associated to the
transition eigenvector.
When this strategy is applied to condensed phase systems many parallel reaction paths may exist.
If the minimization process is brusque during the scanning,
the system may fall down into a parallel valley of the reaction lower in energy.
This would provoke a discontinuity in the energy profile meaning that reactants and products are not actually connected.
To avoid this hysteresis
Some authors
calculate the reaction path from reactants to products ad back to reactants many
times [99] until the obtained energy profile is unique.




Next: Intrinsic reaction coordinate
Up: Reaction path
Previous: Reaction path
Contents
Xavier Prat Resina
2004-09-09