

Next: Long range interactions
Up: Molecular Mechanics
Previous: Molecular Mechanics
Contents
Energy terms: bonded and non-bonded
We are going to assume that the energy of the system is separable in different terms.
The usual separation is the following
There are many expressions for every term, some force fields incorporate crossing terms to account
for the coupling between two different interaction types.
However, we are interested in those force fields that are specialized in the treatment of biomolecules.
In this case the common energy terms are
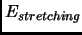 |
 |
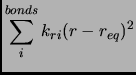 |
(2.53) |
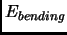 |
 |
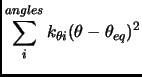 |
(2.54) |
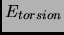 |
 |
![$\displaystyle \sum_{i}^{dihedr} \frac{V_{i}}{2}[1+cos(n\phi-\gamma)]$](img177.png) |
(2.55) |
 |
 |
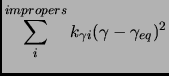 |
(2.56) |
where 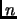 in equation 1.55 is the multiplicity of the conformation.
And for the non-bonded interactions
in equation 1.55 is the multiplicity of the conformation.
And for the non-bonded interactions
the weighting function 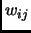 is typically set to zero for atoms
is typically set to zero for atoms 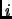 and
and 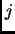 connected by a bond or angle and
connected by a bond or angle and 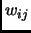 ranges from
ranges from
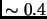 to
to 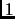 for 1-4 interactions.
for 1-4 interactions.
The general combination rules for Van der Waals parameters between two atoms 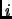 and
and 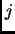 are
are
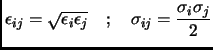 |
(2.59) |
Assuming this separation of the energy the set of parameters 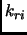 ,
,
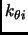 ,
, 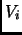 ,
, 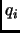 ,
,
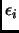 define
a specific force field.
If every different atom had its own set of parameters the amount of parameters to optimize
would be huge. To simplify this task the concept of atom type is used.
The atom type idea is based on the common chemical intuition of transferability. For example, all the sp3
carbon atoms in an alkylic chain will have the same set of parameters because its chemical behavior is approximately
the same in different length chains.
However every force field defines its own set of atom types, so the parameters for a certain atom in a force field
are not usually transferable to another force field.
define
a specific force field.
If every different atom had its own set of parameters the amount of parameters to optimize
would be huge. To simplify this task the concept of atom type is used.
The atom type idea is based on the common chemical intuition of transferability. For example, all the sp3
carbon atoms in an alkylic chain will have the same set of parameters because its chemical behavior is approximately
the same in different length chains.
However every force field defines its own set of atom types, so the parameters for a certain atom in a force field
are not usually transferable to another force field.




Next: Long range interactions
Up: Molecular Mechanics
Previous: Molecular Mechanics
Contents
Xavier Prat Resina
2004-09-09
![]() and
and ![]() are
are
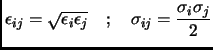
![]() ,
,
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,
![]() define
a specific force field.
If every different atom had its own set of parameters the amount of parameters to optimize
would be huge. To simplify this task the concept of atom type is used.
The atom type idea is based on the common chemical intuition of transferability. For example, all the sp3
carbon atoms in an alkylic chain will have the same set of parameters because its chemical behavior is approximately
the same in different length chains.
However every force field defines its own set of atom types, so the parameters for a certain atom in a force field
are not usually transferable to another force field.
define
a specific force field.
If every different atom had its own set of parameters the amount of parameters to optimize
would be huge. To simplify this task the concept of atom type is used.
The atom type idea is based on the common chemical intuition of transferability. For example, all the sp3
carbon atoms in an alkylic chain will have the same set of parameters because its chemical behavior is approximately
the same in different length chains.
However every force field defines its own set of atom types, so the parameters for a certain atom in a force field
are not usually transferable to another force field.